 |
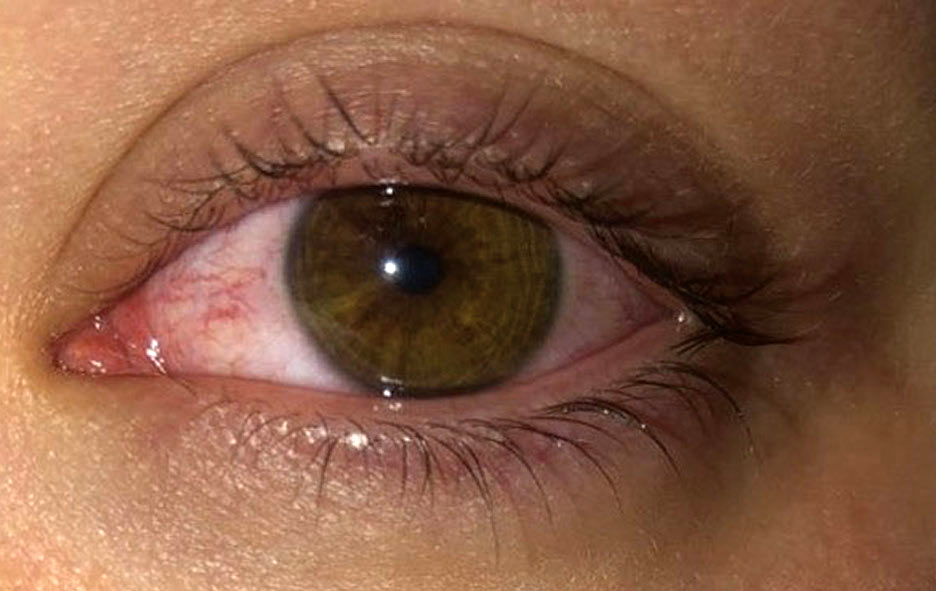
| More efforts are needed to educate patients on safer contact lens wear and handling. Photo: Jennifer Harthan, OD. Click image to enlarge. |
Everyone who prescribes contact lenses knows all too well the challenges inherent in trying to get patients to abide by your wear-and-care instructions. Too often, it might not happen until after an adverse event has already occurred. The Contact Lens Risk Survey, designed to inform clinicians of the risk of soft lens complications, shows some potential avenues to shaping behavior patterns. In a recent study, researchers sought to determine if targeted education can influence the behaviors and scores of soft lens wearers via the survey.
In this multicenter, prospective, case-controlled study, 41 soft lens wearers with symptomatic red eye between the ages of 18 and 39, along with 71 controls, were analyzed. Participants completed the survey and were provided targeted patient education at baseline, one and six months. The study authors found that targeted patient education can influence the behaviors of soft lens wearers and that patients who experienced a recent adverse event may be more receptive to education than healthy wearers.
Responses to topics such as lens case replacement frequency trended in the direction of improved behaviors but did not achieve statistical significance. Overnight wear of contact lenses seemed to worsen in cases, but the majority of participants (83%) reported never or infrequently sleeping overnight in lenses at baseline.
“Lens care behaviors appear to be amenable to change, perhaps because they are concrete, actionable, unlikely to impact overall lifestyle and easily relatable to successful lens wear,” the authors explained in their paper on the work. “In contrast, living environment is a multifaceted risk factor and not likely to be perceived by the patient as a realistic contact lens management option. Instead, a provider might probe further to identify steps for the individual patient that temper the risk of their living environment. For example, college students living in high-density living quarters may benefit from heightened awareness of hygiene, water exposure when showering and closed eye lens wear.”
Improvement in overall behavior was observed during the follow-up period. To sustain this, periodic educational reinforcement may be beneficial, such as through social media, e-mail or patient portals between office visits, the authors suggested.
“A revised patient education tool that emphasizes modifiable risk factors, particularly high risk and low adherence items such as overnight wear and water exposure, may help to reduce the overall risk to patients and improve the safety profile,” the authors concluded.
Lam D, Wagner H, Zimmerman AB, et al. Change in risk score and behaviors of soft contact lens wearers after targeted patient education. Eye Contact Lens. May 17, 2022. [Epub ahead of print]. |

