 |
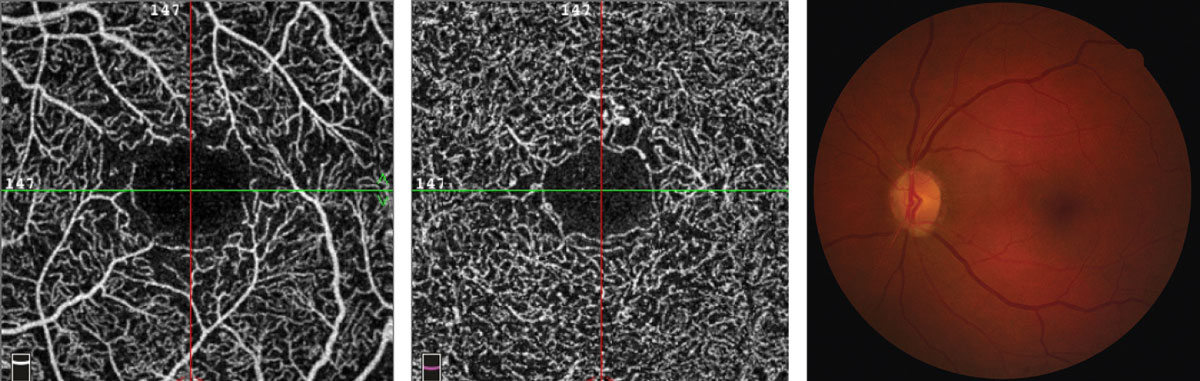
This 65-year-old female has enlarged foveal avascular zone with indistinct borders, capillary nonperfusion surrounding the fovea with scattered areas devoid of flow and microaneurysms. Photo: Julie Rodman, OD. Click image to enlarge. |
Vascular dysfunction is a hallmark of diabetes and diabetic retinopathy, but researchers believe the microvasculature might be affected even at the prediabetic stage in individuals 65 and older. A Japanese team recently obtained data from a community-dwelling elderly population and discovered that microvasculature changes can occur before a definitive diabetes diagnosis.
Their cross-sectional study included a total of 452 eyes without retinal pathologies of 301 elderly patients. Eyes were categorized into non-DM (50%, HbA1c ≤5.7%), pre-DM (39%, HbA1c between 5.7% and 6.4%) and DM (11%, HbA1c ≥6.5% or on treatment) groups.
The researchers conducted fundus photography, swept-source OCT-A and comprehensive systemic examinations. The vessel density (VD) and foveal avascular zone in the superficial and deep retinal microvasculature were investigated for their association with DM staging.
Superficial VD mean values in the non-DM, pre-DM and DM groups were 35.2%, 34.9% and 34.8%, respectively. The researchers noted that superficial VD in pre-DM was equivalent to that of DM patients but significantly lower than the non-DM group (-0.19 difference).
Deep VD mean values in the non-DM, pre-DM and DM groups were 35.0%, 35.0% and 34.4%, respectively. Deep VD in pre-DM was equivalent to that of non-DM patients but significantly higher than the DM group (0.31 difference).
This study’s data was in line with previous reports which did not find a significant change in foveal avascular zone in the pre-DM or DM groups.
As the data was obtained from an elderly Japanese population living in a district of Tokyo, the researchers noted that younger populations, other ethnicities and other geographies must also be investigated for generalization. Also, a larger sample size could help further clarify the differences in microvascular parameters among non-DM, pre-DM and DM patients.
“Although further investigations are necessary in other populations with different backgrounds, our data indicate that monitoring retinal microvascular density using swept-source OCT-A may have a clinical value in patients with pre-DM,” they concluded in their paper.
Wang Y, Toyama T, Hashimoto Y, et al. Association of prediabetes with retinal microvasculature on swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography in the elderly. Retina. January 20, 2022. [Epub ahead of print]. |

