 |
|
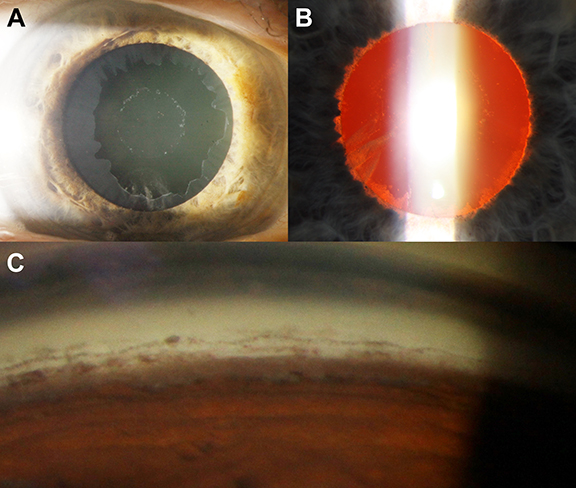
The results of this study suggest that apparently fellow eyes free of pseudoexfoliation of patients with early-stage PXG did not have significant radial peripapillary capillary VD or RNFL loss. Photo: Henrietta Wang, BOptom, MPH, and Jack Phu, OD, PhD. Click image to enlarge. |
Pseudoexfoliation syndrome is a major risk factor for developing glaucoma and is the most common cause of secondary open-angle glaucoma. The development of glaucomatous changes in normotensive eyes suggests that an interaction of different mechanisms is involved in the pathogenesis of pseudoexfoliation glaucoma (PXG). With the development of OCT-A technology, interest in investigating the microcirculation in the optic nerve head and macular region has increased. Thus, vessel density (VD) measurements are being used both as an additional parameter in diagnosis and follow-up and to garner clues about the vascular theory in the pathogenesis of glaucoma. A recent study based in Turkey evaluated the radial peripapillary capillary VD and macular superficial VD parameters of unilateral PXG patients, both in the eyes in the preperimetric or early stage of glaucoma and the fellow eyes that were not clinically affected but most likely in the preclinical phase of glaucoma. While PXG eyes had lower RNFL and radial peripapillary capillary VD values than in both the fellow eyes and the control group, there was no difference in either RNFL thickness or radial peripapillary capillary VD in fellow eyes compared to the control group.
This cross-sectional study included 28 eyes with PXG and 28 nonglaucomatous, pseudoexfoliation-free fellow eyes of 28 patients and 28 eyes of 28 healthy participants. In sector-based evaluation, the decrease in radial peripapillary capillary VD in PXG eyes was evident in the nasal superior, nasal inferior, inferonasal and superonasal sectors, while RNFL thickness spread from the nasal towards the temporal sectors. While perifoveal GCC differed from both fellow and control eyes, there was no significant difference in macular VD parameters among the groups.
“These findings do not support the hypothesis that vascular deterioration may be a precursor to structural loss,” the study authors concluded in their paper, which was published in the Journal of Glaucoma.
Solmaz N, Oba T. Peripapillary and macular vessel density in unilateral early pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. J Glaucoma. August 15, 2024. [Epub ahead of print]. |


