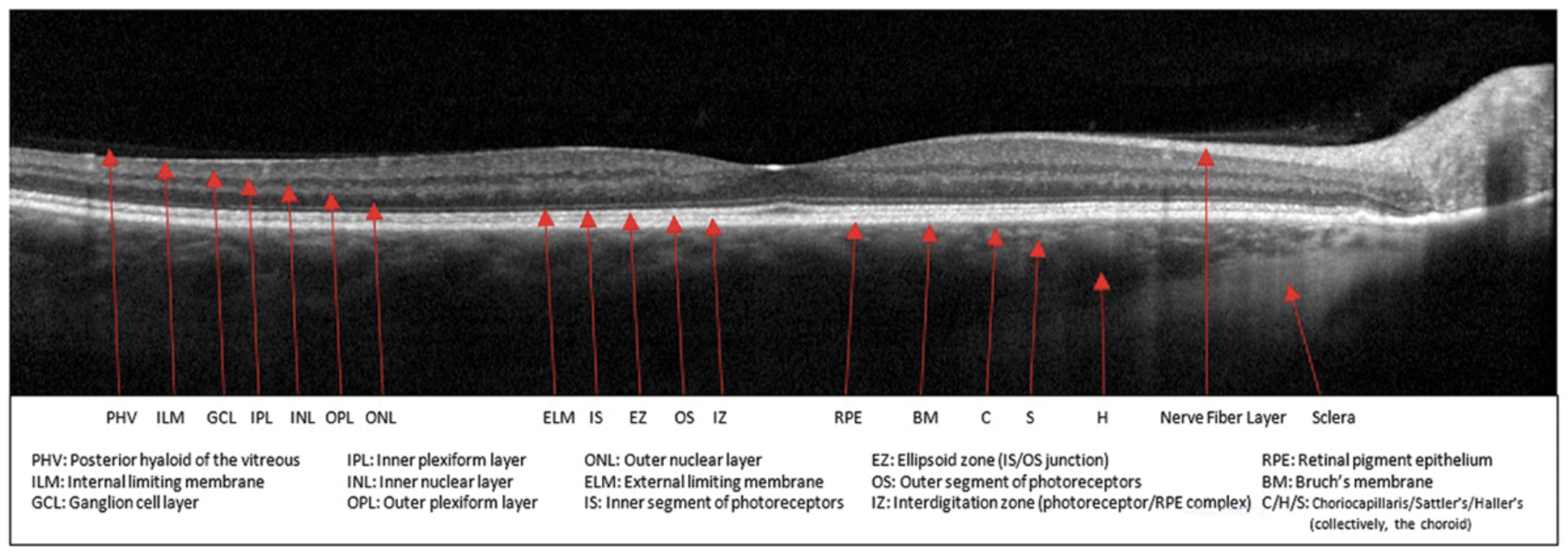
 |
| Longitudinal measurements of inner nuclear layer thickness may be effective when following disease progression in patients with advanced-stage glaucoma. Photo: Sara Weidmayer, OD |
The ability to detect progression in eyes with advanced glaucoma is challenging because of the known limitations of increased measurement variability or when commonly used structural and functional parameters reach their minimal measurable limit (known as the floor effect). At the 2022 ARVO meeting in Denver, researchers shared that longitudinal measurements of inner nuclear layer thickness may be effective when following disease progression in patients with advanced-stage glaucoma where circumpapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness is no longer useful.
The study included 23 eyes of 23 patients (12 with early/moderate glaucoma and 11 with advanced glaucoma) with ≥four visits. Subjects in the early/moderate group had average circumpapillary RNFL thicknesses ≥60µm, and subjects in the advanced group had average circumpapillary RNFL thicknesses ≤60µm. All participants underwent comprehensive ophthalmic examination, visual field testing and spectral domain OCT optic nerve head and macula scans.
At baseline, a statistically significant difference between groups was detected in mean deviation, circumpapillary RNFL and ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer (GCIPL) thicknesses. In early/moderate glaucoma eyes, the rate of change was significantly different than a zero slope for circumpapillary RNFL thickness, cup-to-disc ratio and GCIPL thickness. Inferior inner nuclear layer thickness was the only inner nuclear layer parameter showing a significant rate of change. However, in the advanced glaucoma group, all parameters (including both global and sectoral inner nuclear layer thicknesses) except for the circumpapillary RNFL showed a significant rate of change.
Original abstract content © Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology 2022.
Shemuelian E, Wollstein G, de los Angeles Ramos Cadena M, et al. Can the inner nuclear layer thickness help detect progression in advanced glaucoma? ARVO 2022 annual meeting. |


