Editor’s Note: As part of our “Year in Review” retrospective, we’ve selected the top 30 news stories of the year and are re-sharing them as we close out 2023. Follow along as we count down to number 1!
This story was originally published October 16, 2023.
No. 12 biggest news story of 2023:
Ocular motility dysfunction can occur when there’s damage to cranial nerves III, IV and VI. This neuropathy is associated with several cardiovascular conditions already on eyecare providers’ radar, such as hypertension, obesity, diabetes and smoking. Importantly, dementia shares these risk factors as well, and a connection between dementia and ocular motor cranial neuropathy (OMCN) has long been speculated. To learn whether OMCN might be a predictor or independent risk factor for dementia, researchers in Korea recently conducted a nationwide cohort study. They found that early-onset OMCN is a strong dementia predictor.
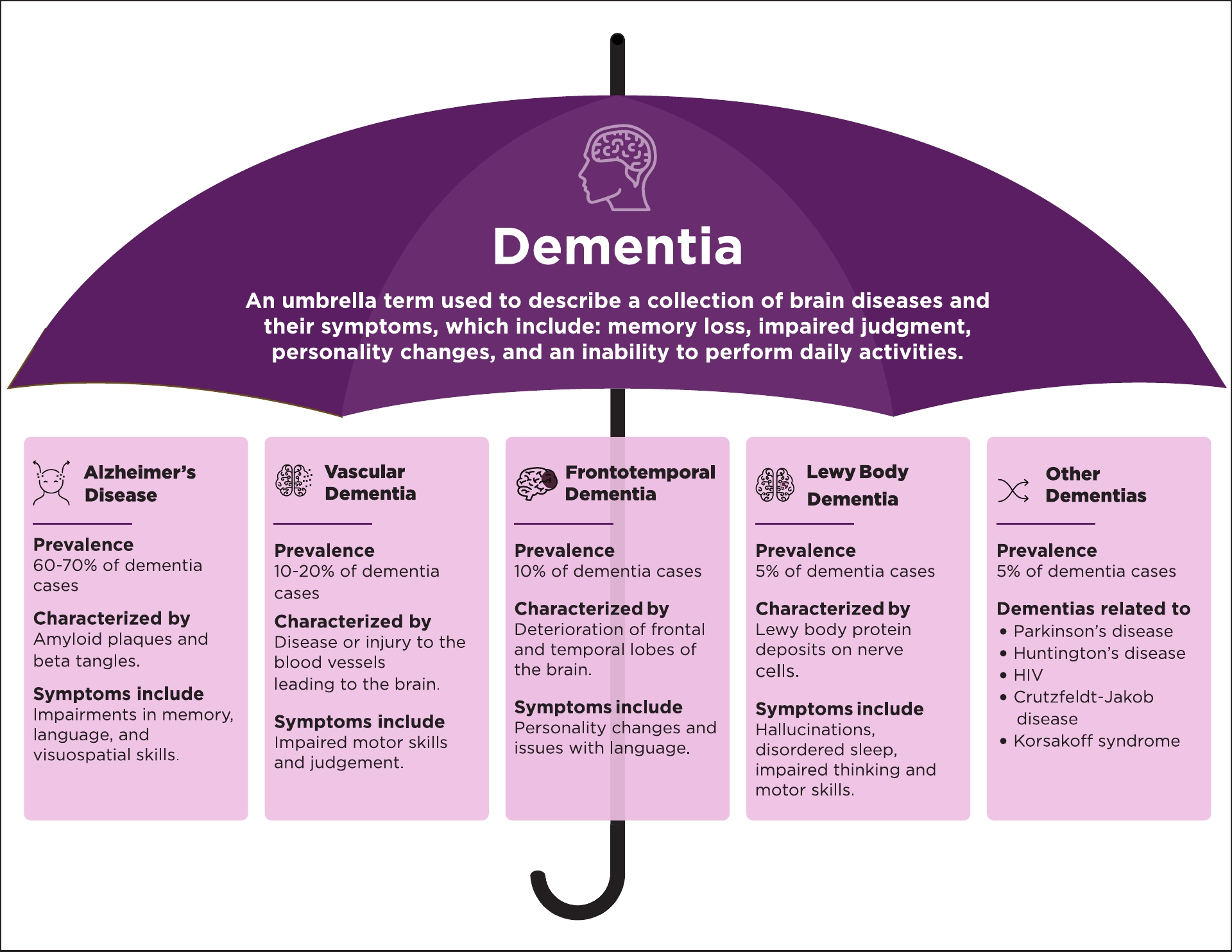 |
| Dementia is characterized by cognitive decline and functional impairment. Modifiable risk factors include lack of exercise, smoking and a poor diet. These factors have important ocular implications as well. Click image to enlarge. |
The final cohort included 19,243 patients and 96,215 age- and sex-matched controls without OMCN. Using the patients’ health records from the Korean National Health Insurance Service, the researchers identified newly diagnosed OMCN by the first claim with a dementia diagnostic code and anti-dementia medications.
They reported that patients with newly diagnosed OMCN had more metabolic comorbidities than non-OMCN patients. Additionally, they found an association between new OMCN and an increased risk for all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia, independent of confounders. Patients under 50 demonstrated a stronger association between all-cause dementia and OMCN than older patients.
The researchers explained in their Ophthalmology paper that the pathogenesis of OMCN isn’t fully understood, but it’s likely to result from a combination of factors. “The most common cause of OMCN is ischemic nerve injury, which may result from conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension and atherosclerosis,” they wrote. “Other causes of OMCN include trauma, infections, inflammation, tumors and autoimmune disorders.” Key mechanisms seem to include vascular damage, inflammation and neurodegeneration.
“Our study presents unprecedented evidence indicating that OMCN, particularly in younger patients, could serve as a strong predictor of cognitive decline, including the onset of Alzheimer’s disease among the vast majority of the national population,” the researchers concluded in their paper. They pointed out the importance of conducting comprehensive neurological examinations in patients presenting with OMCN, including brain imaging and neuropsychological evaluation.
Kim J, Han K, Jung J, et al. Early-onset ocular motor cranial neuropathy is a strong predictor of dementia: a nationwide, population-based cohort study. Ophthalmology 2023. [Epub ahead of print]. |

